Weather Nowcasting with Flowdapt¶
Introduction¶
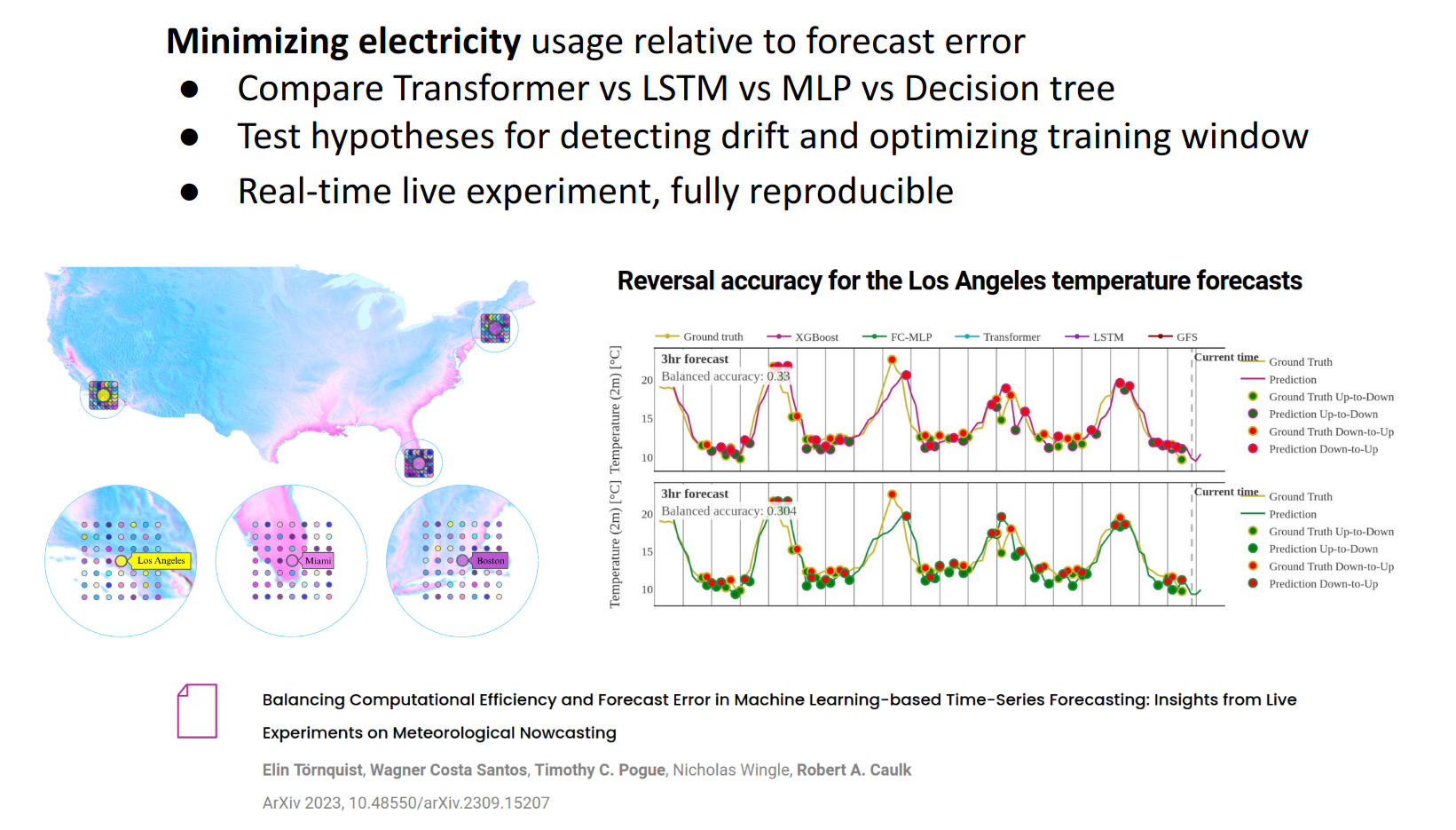
Emergent Methods performed a large-scale nowcasting experiment in real-time to study the relationship between forecast accuracy and computational efficiency. The full report with all results are detailed in the companion paper. The experimental code is simplified in the Nowcast repository as an example for how flowdapt can be used to build a real-time adaptive modeling system. Here we provide an overview of how the components are constructed.
Train workflow¶
The train workflow gets the city iterable to parameterize the train_pipeline across the desired number of cities. The train workflow does not worry about getting data, it pulls the latest data available, which is already prepped by the data update workflow.
kind: workflow
metadata:
name: train
annotations:
group: nowcast
spec:
stages:
- name: get_city_model_iterable
target: flowdapt_nowcast_plugin.stages.get_city_model_iterable
resources:
cpus: 0.5
- name: train_pipeline
target: flowdapt_nowcast_plugin.stages.train_pipeline
type: parameterized
depends_on:
- get_city_model_iterable
resources:
gpus: 1
Inference workflow¶
The inference workflow gets the city iterable to parameterize the predict_pipeline across the desired number of cities. The inference workflow does not worry about getting data, it pulls the latest data available, which is already prepped by the data update workflow.
kind: workflow
metadata:
name: predict
annotations:
group: nowcast
spec:
stages:
- name: get_city_model_iterable
target: flowdapt_nowcast_plugin.stages.get_city_model_iterable
resources:
cpus: 0.5
- name: predict_pipeline
target: flowdapt_nowcast_plugin.stages.predict_pipeline
type: parameterized
depends_on:
- get_city_model_iterable
resources:
cpus: 4
Data update workflow¶
The data update workflow fetches data for the target cities, as well as auxiliary cities that may be used to help improve accuracy on the target cities. It stores the data and prepares the features so that the train and inference workflows are focused entirely on training or inferencing at low-latency.
kind: workflow
metadata:
name: create_features
annotations:
group: nowcast
spec:
stages:
- name: create_parameterization_lists
target: flowdapt_nowcast_plugin.stages.create_parameterization_lists
resources:
cpus: 0.5
- name: get_unique_city_iterable
target: flowdapt_nowcast_plugin.stages.get_unique_city_iterable
depends_on:
- create_parameterization_lists
resources:
cpus: 0.5
- name: get_and_publish_data
target: flowdapt_nowcast_plugin.stages.get_and_publish_data
type: parameterized
depends_on:
- get_unique_city_iterable
resources:
cpus: 1
- name: get_target_city_iterable
target: flowdapt_nowcast_plugin.stages.get_target_city_iterable
depends_on:
- get_and_publish_data
resources:
cpus: 0.5
- name: construct_dataframes
target: flowdapt_nowcast_plugin.stages.construct_dataframes
type: parameterized
depends_on:
- get_target_city_iterable
resources:
cpus: 1
Configuration¶
kind: config
metadata:
name: main
annotations:
group: nowcast
spec:
selector:
type: annotation
value:
group: nowcast
data:
study_identifier: "openmeteo_test"
# Study control parameters
n_days: 50
neighbors: 2
radius: 150
prediction_points: 1
target_horizon: 6
city_data_path: "flowdapt_nowcast_plugin/data/uscities.csv"
model: "XGBoostRegressor"
cities: ['Los Angeles', 'Miami']
targets: ["temperature_2m", "windspeed_10m", "cloudcover"]
# training parameters
model_train_parameters:
# xgboost parameters
n_jobs: 4
n_estimators: 200
# device: "cuda"
# tree_method: "hist"
alpha: 0.5
min_child_weight: 5
learning_rate: 0.1
eval_metric: "rmse"
max_depth: 6
verbosity: 1
lookback: 6
# # neural net parameters for PyTorch variants
# epochs: 10 # 35
# batch_size: 64
# lookback: 6
# hidden_dim: 2048
# shuffle: True
# num_threads: 4
extras:
weight_factor: 0.9
di_threshold: 5.0
num_points: 1200 # 3500
artifact_only: true
data_split_parameters:
test_size: 256
shuffle: false
Running Nowcast¶
After you installed flowdapt with pip install flowdapt and flowctl with pip install flowctl, you can clone the Nowcast Plugin repository and install:
git clone https://gitlab.com/emergentmethods/flowdapt-nowcast-plugin.git
cd flowdapt-nowcast-plugin
poetry install
Now you can apply your resources:
flowctl apply -p flowdapt_nowcast_plugin/workflows
flowctl apply -p flowdapt_nowcast_plugin/configs
You can run the workflows manually if you wish with flowctl run create_features and flowctl run train_pipeline and flowctl run predict_pipeline. However, these are typically scheduled with the included triggers:
flowctl apply -p flowdapt_nowcast_plugin/triggers
Further, you can use the flowdapt_sdk to automate these processes, or to ask for the latest predictions. This functionality is exemplified in the python_driver.py file.
Details about the train_pipeline, predict_pipeline, and create_features stages can be found in the Nowcast Plugin repository.